What is the behavior of partition walls, widely used in offices, in the event of an earthquake? What does the current legislation establish in this regard? Is it possible to have products that guarantee greater safety in the event of seismic actions?
Universal Selecta, which has always been attentive to the certification of its walls, answered these questions and conducted a research to identify and codify a methodological scheme for seismic behavior tests to be applied to a mobile wall system.
The tests performed made it possible to achieve the ambitious goal of obtaining the CE marking pursuant to CPR (EU) 305/2011 for all lines of Universal Selecta walls.
The research results are well summarized in this video.
Universal Selecta conducted research with the aim of analyzing the behavior of partition systems subject to an earthquake.
The research was carried out with a view to the “performance based design” design philosophy according to which the performance of a building against an earthquake is defined not only by its structural elements, such as beams and pillars, but also not structural elements, such as movable walls.
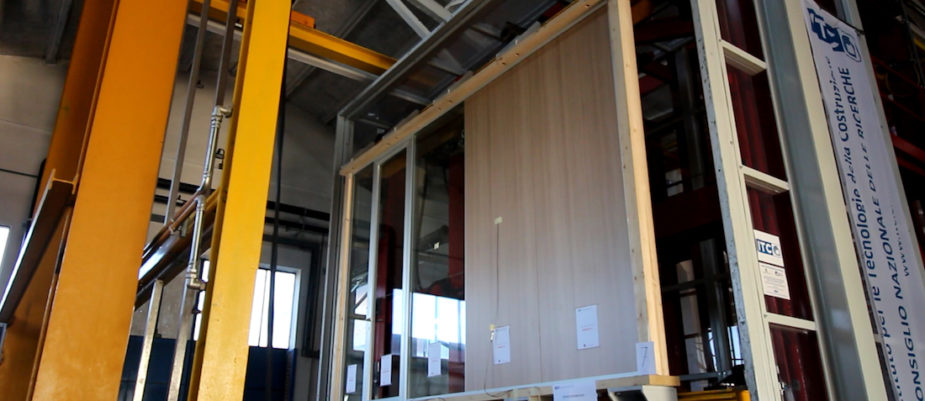
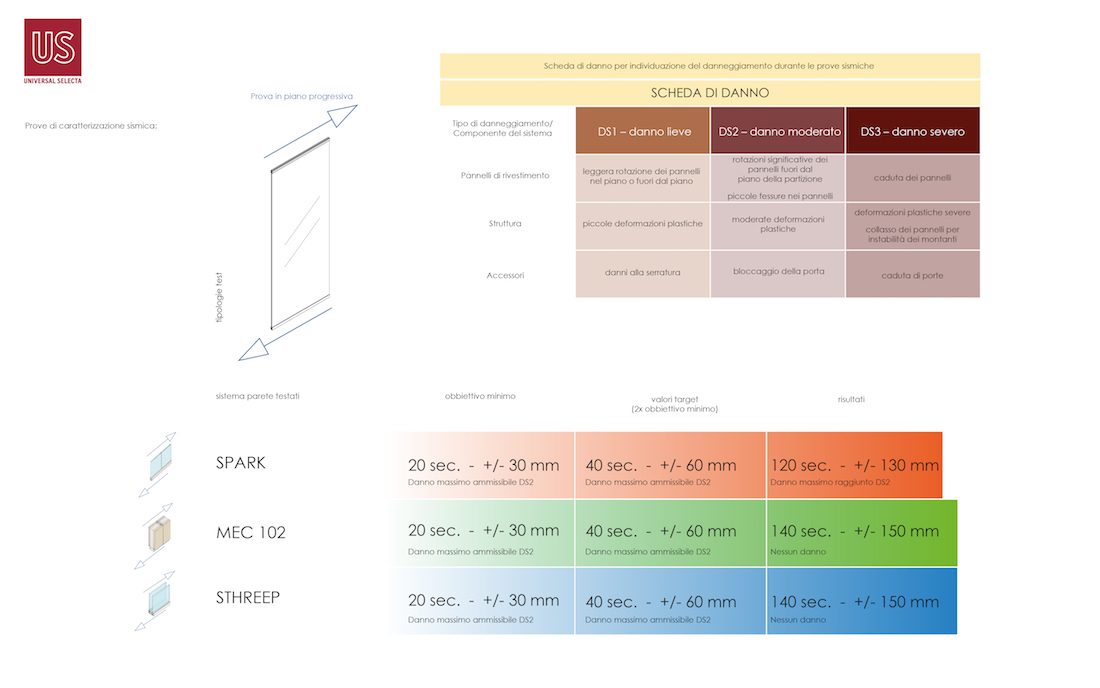
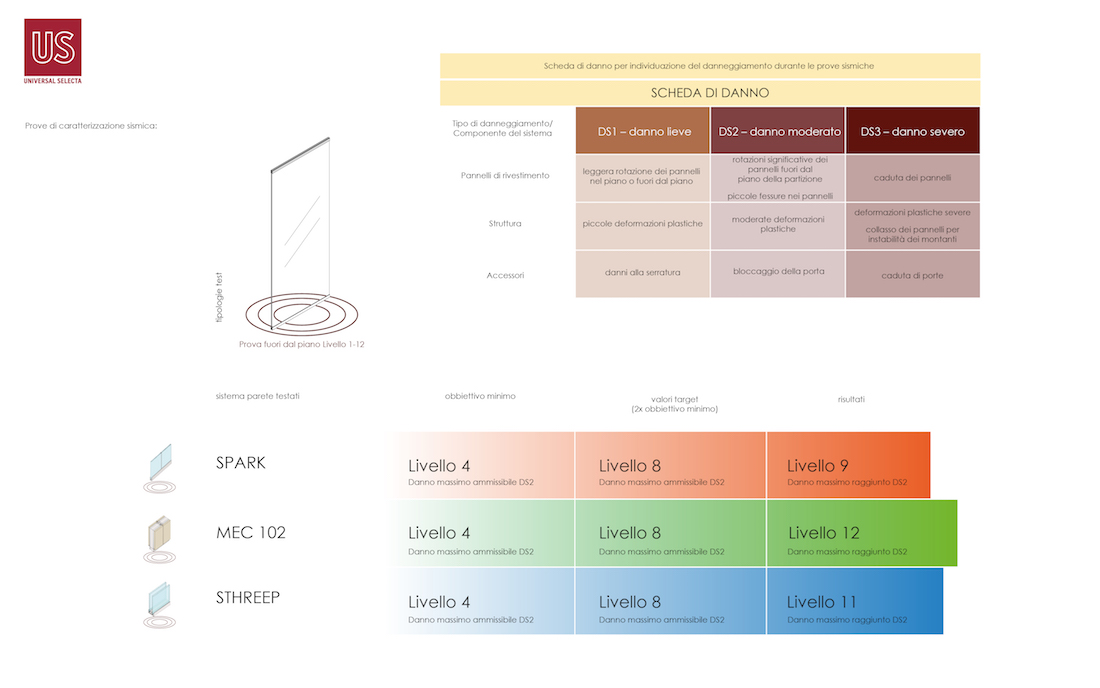
The verification of the parameters characterizing the seismic behavior of the partitions can be carried out by means of experimental tests on full-scale components, through the use of a special equipment for seismic tests of flat elements. The tests were carried out at the ITC-CNR laboratory in San Giuliano Milanese, the only structure in Italy equipped with the necessary equipment for carrying out the tests.
The test methods were refined starting from international references (including AAMA 501.6 for the crescendo test and AC156 for dynamic tests); these methods have already been included in the revision of an EAD document concerning the issue of ETA, and therefore the subsequent CE marking, of ventilated facades.
Final remarks
The execution of the tests on the Spark, Sthreep and MEC102 wall systems samples showed a resistance to seismic actions that was much higher than the limits imposed by the NTC, to an extent ranging from 160% to 500% depending on the type of test and the tested product.
Text edited by Universal Selecta